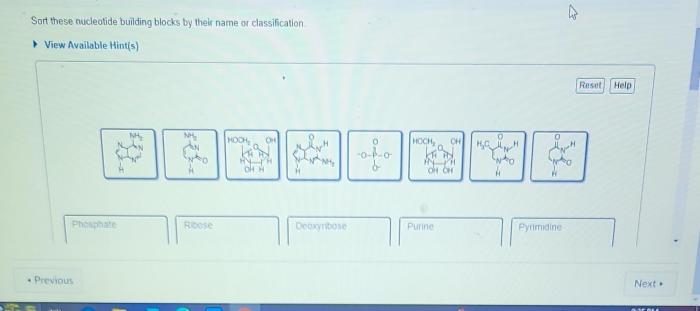
Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classification – Nucleotide building blocks, the fundamental units of DNA and RNA, play a pivotal role in the intricate tapestry of life. This discourse embarks on an exploration of their classification and nomenclature, delving into the intricacies of their chemical structures and functional groups.
As we unravel the intricacies of nucleotide building blocks, we will uncover the systematic approach to their classification, examining the distinct types of nucleotides and their corresponding chemical compositions. We will decipher the naming conventions employed, recognizing the significance of these names in reflecting the chemical properties of each nucleotide.
Nucleotide Building Blocks
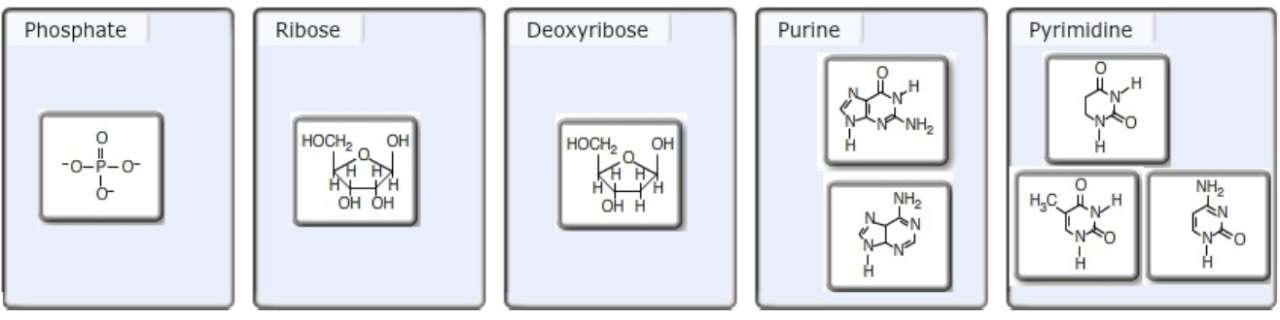
Nucleotide building blocks are the fundamental units of nucleic acids, which are essential for storing and transmitting genetic information in living organisms. These building blocks consist of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Classification of Nucleotide Building Blocks
Nucleotide building blocks can be classified based on the type of nitrogenous base they contain. There are two main types of nitrogenous bases: purines and pyrimidines.
Purines are double-ringed structures that include adenine (A) and guanine (G). Pyrimidines are single-ringed structures that include cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
In addition to their classification based on nitrogenous base, nucleotide building blocks can also be classified based on the type of sugar they contain. Nucleotides that contain ribose sugar are called ribonucleotides, while those that contain deoxyribose sugar are called deoxyribonucleotides.
Nomenclature of Nucleotide Building Blocks
The nomenclature of nucleotide building blocks is based on the type of nitrogenous base and the type of sugar they contain. For example, the nucleotide building block that contains adenine and ribose sugar is called adenosine.
The names of nucleotide building blocks are also often abbreviated using a single letter code. For example, adenosine is abbreviated as A, guanosine is abbreviated as G, cytidine is abbreviated as C, thymidine is abbreviated as T, and uridine is abbreviated as U.
Sorting Nucleotide Building Blocks: Sort These Nucleotide Building Blocks By Their Name Or Classification
| Name | Classification | Chemical Structure | Functional Groups |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adenosine | Purine ribonucleotide | [Chemical structure of adenosine] | Adenine, ribose, phosphate |
| Guanosine | Purine ribonucleotide | [Chemical structure of guanosine] | Guanine, ribose, phosphate |
| Cytidine | Pyrimidine ribonucleotide | [Chemical structure of cytidine] | Cytosine, ribose, phosphate |
| Thymidine | Pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide | [Chemical structure of thymidine] | Thymine, deoxyribose, phosphate |
| Uridine | Pyrimidine ribonucleotide | [Chemical structure of uridine] | Uracil, ribose, phosphate |
Examples of Nucleotide Building Blocks
- Adenosine is a purine ribonucleotide that is involved in a variety of cellular processes, including energy metabolism and signal transduction.
- Guanosine is a purine ribonucleotide that is involved in protein synthesis and cell division.
- Cytidine is a pyrimidine ribonucleotide that is involved in DNA synthesis and repair.
- Thymidine is a pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide that is involved in DNA synthesis.
- Uridine is a pyrimidine ribonucleotide that is involved in RNA synthesis and metabolism.
FAQ
What is the significance of functional groups in nucleotide building blocks?
Functional groups determine the chemical reactivity and interactions of nucleotides, influencing their roles in biological processes.
How does the classification of nucleotides aid in understanding their biological functions?
Classification provides a systematic framework for organizing nucleotides based on their structural and chemical properties, facilitating the study of their specific roles in cellular processes.
What are the key differences between DNA and RNA nucleotides?
DNA nucleotides contain deoxyribose sugar, while RNA nucleotides contain ribose sugar, leading to structural and functional variations.