The art-labeling activity structure of a cardiac muscle fiber unveils the intricate histological organization that underlies the rhythmic contractions of the heart. Delving into the microscopic realm, this activity invites us to explore the unique structural features that enable cardiac muscle fibers to perform their vital function.
This exploration will illuminate the arrangement of myofibrils, the organization of sarcomeres, and the specialized structures that facilitate coordinated contractions. By unraveling the histological tapestry of cardiac muscle fibers, we gain insights into the remarkable adaptations that allow the heart to sustain life.
Anatomy and Structure of a Cardiac Muscle Fiber
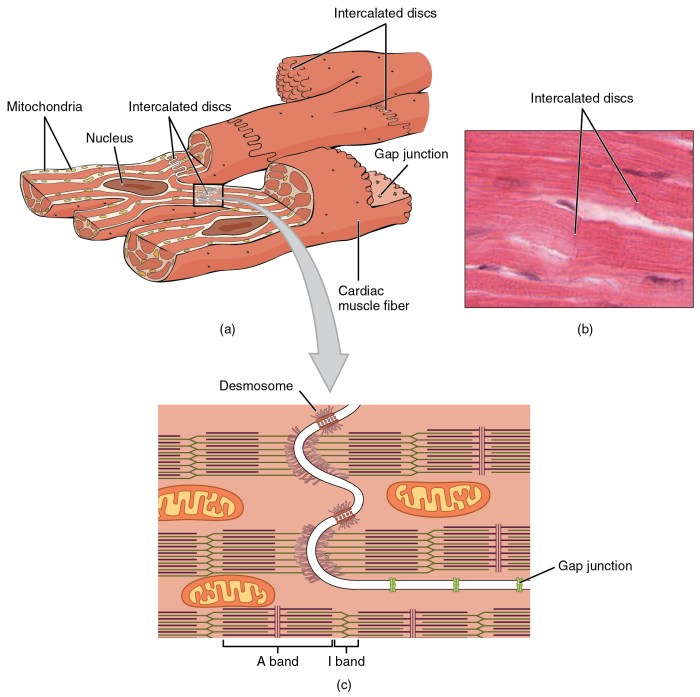
Cardiac muscle fibers are specialized cells that form the contractile units of the heart. They exhibit a unique histological structure that enables them to perform rhythmic contractions throughout life.
Organization of Myofibrils
Cardiac muscle fibers contain numerous myofibrils, which are organized in a parallel arrangement. Each myofibril is composed of repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the fundamental contractile units of muscle.
Arrangement of Sarcomeres
Sarcomeres are arranged in a regular pattern within cardiac muscle fibers. The A-bands represent the thick myosin filaments, while the I-bands represent the thin actin filaments. The Z-lines mark the boundaries of each sarcomere.
Functional Aspects of Cardiac Muscle Fibers: Art-labeling Activity Structure Of A Cardiac Muscle Fiber
Unique Properties
Cardiac muscle fibers possess several unique properties that allow them to contract rhythmically. They exhibit automaticity, the ability to generate electrical impulses spontaneously, and are refractory to additional stimuli during the contraction phase.
Intercalated Discs
Intercalated discs are specialized junctions between cardiac muscle fibers. They facilitate coordinated contractions by allowing electrical and mechanical signals to pass from one fiber to another.
Electrical Properties
Cardiac muscle fibers have distinct electrical properties. The resting membrane potential is more negative than in skeletal muscle, and the action potential is longer in duration. These properties contribute to the slow and sustained contractions of the heart.
Regulation of Cardiac Muscle Contraction
Calcium Ions
Calcium ions play a crucial role in triggering and controlling cardiac muscle contraction. The influx of calcium ions through L-type calcium channels initiates the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which binds to troponin and initiates muscle contraction.
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system modulates cardiac muscle function through the release of neurotransmitters. Sympathetic stimulation increases heart rate and contractility, while parasympathetic stimulation decreases heart rate and contractility.
Histological Techniques for Studying Cardiac Muscle Fibers
Staining Techniques, Art-labeling activity structure of a cardiac muscle fiber
Histological staining techniques, such as hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, allow for the visualization of the general structure of cardiac muscle fibers. Masson’s trichrome staining can highlight collagen and fibrosis.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry can be used to identify specific proteins within cardiac muscle fibers. Antibodies specific to a target protein are used to visualize its localization and expression levels.
Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy provides high-resolution images of the ultrastructure of cardiac muscle fibers. It can reveal details of the myofibril organization, sarcomere structure, and other cellular components.
Clinical Applications of Cardiac Muscle Fiber Analysis
Clinical Significance
Analyzing cardiac muscle fiber structure and function has clinical significance in diagnosing and managing cardiac diseases. Abnormalities in fiber size, shape, and organization can indicate various pathological conditions.
Cardiac Muscle Biopsy
Cardiac muscle biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of heart tissue for examination. It can help diagnose conditions such as cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, and arrhythmias.
Cardiac Muscle Fiber Engineering
Cardiac muscle fiber engineering holds potential for regenerative medicine. Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells and tissue engineering techniques to create new cardiac muscle tissue for transplantation.
Expert Answers
What is the unique feature of cardiac muscle fibers?
Cardiac muscle fibers possess intercalated discs, specialized structures that facilitate electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cells, enabling coordinated contractions.
How does calcium regulate cardiac muscle contraction?
Calcium ions trigger and control cardiac muscle contraction. When calcium enters the cell, it binds to troponin, initiating a conformational change that allows myosin to bind to actin and generate force.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in cardiac muscle function?
The autonomic nervous system modulates cardiac muscle function by releasing neurotransmitters that bind to receptors on the surface of cardiac muscle cells, influencing heart rate, contractility, and conduction velocity.