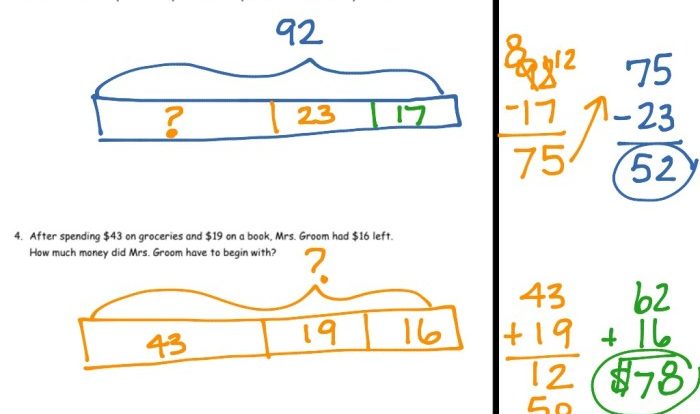
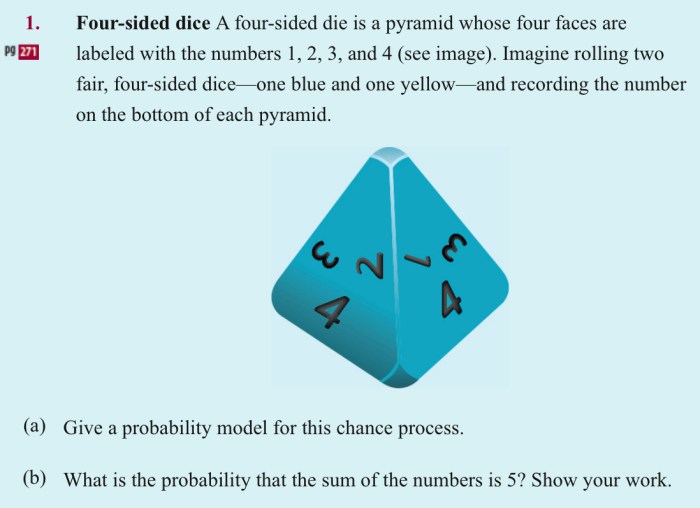
A four sided die is a pyramid whose four faces – A four-sided die, also known as a tetrahedron, is a pyramid with four faces. This unique shape gives the die its distinctive properties and makes it a versatile tool in various applications. In this article, we will explore the geometric, historical, mathematical, and cultural aspects of a four-sided die.
The base of the die is a square, and the four faces are equilateral triangles. The angles between the faces are all 90 degrees, and the edges are all equal in length. This regular shape makes the die easy to roll and ensures that each face has an equal chance of landing face up.
Four-Sided Dice: A Comprehensive Analysis

A four-sided die, also known as a tetrahedron, is a unique and versatile geometric shape with a rich history and diverse applications. This article explores the geometric properties, historical evolution, mathematical analysis, applications, and cultural significance of four-sided dice, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating object.
Geometric Properties of a Four-Sided Die
A four-sided die is a three-dimensional shape with four triangular faces. It is a type of pyramid, with a triangular base and three other triangular faces that meet at a single point, known as the apex. The base and faces of the die form the surface of the pyramid, while the edges and vertices define its shape and symmetry.
Base and Faces
The base of a four-sided die is a triangle, and the other three faces are also triangles. These faces are congruent, meaning they have the same shape and size. The base and faces together form the surface of the die.
Edges and Vertices, A four sided die is a pyramid whose four faces
A four-sided die has six edges, which are the line segments where two faces meet. It also has four vertices, which are the points where three edges meet. The edges and vertices define the shape and symmetry of the die.
Angles and Symmetry
The angles of a four-sided die are all equal to 60 degrees. This is because the base and faces of the die are all equilateral triangles. The die also has rotational symmetry, meaning it can be rotated around its apex and still look the same.
Historical Evolution of Four-Sided Dice
Four-sided dice have a long and rich history, dating back to ancient times. The earliest known dice were made from animal bones or stones, and were used for gambling and divination.
Ancient Dice
Some of the earliest known dice have been found in archaeological sites in Egypt and Mesopotamia, dating back to around 3000 BC. These dice were typically made from bone or ivory, and were often used for gambling or divination.
Evolution of Materials and Manufacturing Techniques
Over time, dice evolved in terms of the materials used to make them and the manufacturing techniques employed. In ancient Greece and Rome, dice were often made from bronze or glass. In medieval Europe, dice were typically made from wood or bone.
Modern Dice
In the modern era, dice are typically made from plastic or resin. They are manufactured using a variety of techniques, including injection molding and 3D printing.
Mathematical Analysis of a Four-Sided Die
The probability distribution of outcomes when rolling a four-sided die is uniform, meaning that each outcome is equally likely. This is because the die is symmetrical, and there is no bias towards any particular outcome.
Probability Distribution
The probability of rolling any given number on a four-sided die is 1/4. This is because there are four possible outcomes, and each outcome is equally likely.
Expected Value and Standard Deviation
The expected value of a four-sided die is 2.5. This is the average value that you would expect to roll over a large number of rolls. The standard deviation of a four-sided die is 1.12.
Fairness of a Four-Sided Die
A four-sided die is considered to be fair if the probability of rolling any given number is 1/4. This means that the die is not biased towards any particular outcome.
Applications of Four-Sided Dice
Four-sided dice are used in a variety of games and activities. They are particularly popular in tabletop role-playing games, where they are used to determine the outcome of actions and events.
Tabletop Role-Playing Games
Four-sided dice are commonly used in tabletop role-playing games, such as Dungeons & Dragons and Pathfinder. In these games, dice are used to determine the outcome of actions and events, such as the success or failure of an attack or the amount of damage caused by a spell.
Other Games and Activities
Four-sided dice are also used in a variety of other games and activities, such as board games, card games, and puzzles. They can also be used for educational purposes, such as teaching children about probability and statistics.
Cultural Significance of Four-Sided Dice: A Four Sided Die Is A Pyramid Whose Four Faces

Four-sided dice have cultural significance in a variety of societies. In some cultures, dice are seen as symbols of luck or fortune, while in others they are associated with gambling or divination.
Symbolism and Beliefs
In some cultures, four-sided dice are seen as symbols of luck or fortune. For example, in Chinese culture, the number four is considered to be lucky, and four-sided dice are often used in gambling and other games of chance.
Role in Folklore, Mythology, and Literature
Four-sided dice have also played a role in folklore, mythology, and literature. For example, in the ancient Greek myth of Jason and the Argonauts, the hero Jason is said to have used a four-sided die to determine the outcome of a battle.
FAQ Summary
What is the probability of rolling a specific number on a four-sided die?
The probability of rolling a specific number on a four-sided die is 1 in 4, or 25%.
What is the expected value of a four-sided die?
The expected value of a four-sided die is 2.5.
Are four-sided dice fair?
Four-sided dice are generally considered to be fair, but there may be slight variations in the manufacturing process that could affect the fairness of a particular die.