Blood types and donation possibilities worksheet a answer key – Embark on an exploration of blood types and donation possibilities with our comprehensive answer key for Worksheet A. Delving into the intricacies of blood compatibility, eligibility criteria, and donation procedures, this guide empowers you with a deeper understanding of this vital aspect of healthcare.
From deciphering the significance of blood antigens to navigating the complexities of blood transfusions, this answer key serves as an invaluable resource for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of blood-related matters.
Blood Types and Compatibility

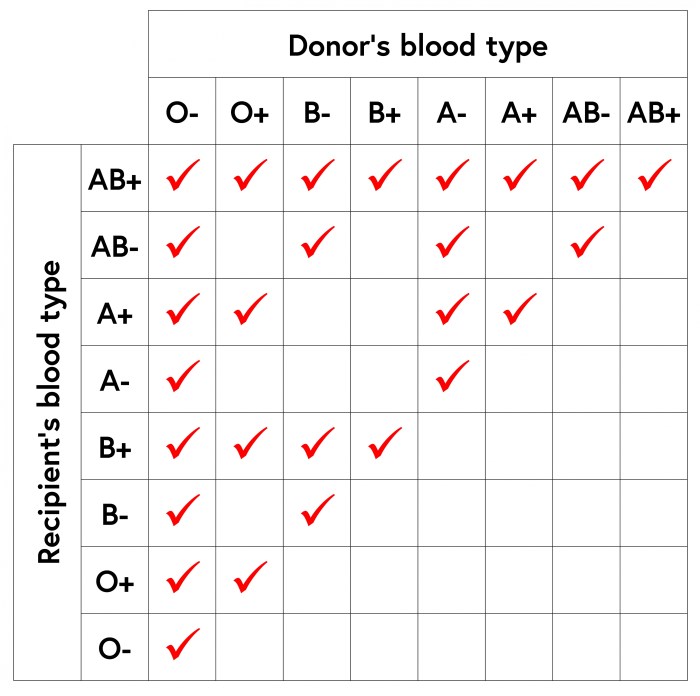
Blood types are classified based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. The main blood group systems are the ABO system and the Rh system. In the ABO system, there are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and O.
People with type A blood have A antigens on their red blood cells, those with type B blood have B antigens, those with type AB blood have both A and B antigens, and those with type O blood have neither A nor B antigens.
In the Rh system, people are either Rh-positive or Rh-negative, depending on the presence or absence of the Rh antigen on their red blood cells.
Blood compatibility refers to the ability of blood from one person to be transfused into another person without causing an adverse reaction. Blood transfusions are only possible between compatible blood types. For example, a person with type A blood can only receive blood from other people with type A or type O blood.
A person with type B blood can only receive blood from other people with type B or type O blood. A person with type AB blood can receive blood from any blood type, and a person with type O blood can only receive blood from other people with type O blood.
Blood Donation Eligibility
To be eligible to donate blood, you must meet certain criteria. These criteria include:
- Being at least 18 years old (or 16 years old with parental consent)
- Weighing at least 110 pounds
- Being in good general health
- Not having any recent illnesses or infections
- Not taking any medications that could interfere with blood donation
- Not having any recent travel to areas with malaria or other blood-borne diseases
If you meet these criteria, you can donate blood every 56 days. The blood donation process is safe and takes about an hour. Before you donate blood, your blood type and compatibility will be determined.
Blood Donation Procedures
The blood donation process involves the following steps:
- Registration: You will be asked to provide your name, address, and contact information. You will also be asked about your medical history and travel history.
- Blood typing: A small sample of your blood will be taken to determine your blood type and compatibility.
- Donation: You will be seated in a comfortable chair and a needle will be inserted into a vein in your arm. The blood will be collected into a sterile bag.
- Recovery: After you have donated blood, you will be given a snack and a drink. You will be asked to rest for a few minutes before leaving the donation center.
It is important to follow the post-donation instructions carefully. These instructions will help you to avoid any complications, such as bruising or infection.
Blood Transfusion Considerations
Blood transfusions are used to replace lost blood or to correct a blood disorder. There are different types of blood transfusions, including:
- Red blood cell transfusions: These transfusions are used to replace lost red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body’s tissues.
- Platelet transfusions: These transfusions are used to replace lost platelets. Platelets help to stop bleeding.
- Plasma transfusions: These transfusions are used to replace lost plasma. Plasma is the liquid part of blood.
Blood transfusions are generally safe, but there are some potential risks and complications. These risks include:
- Allergic reactions
- Hemolytic reactions
- Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)
- Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
The risks of blood transfusions can be minimized by carefully matching the donor’s blood to the recipient’s blood. Blood transfusions are an important medical treatment, and they can save lives.
Quick FAQs: Blood Types And Donation Possibilities Worksheet A Answer Key
What is the significance of blood antigens?
Blood antigens play a crucial role in determining blood compatibility. They are proteins present on the surface of red blood cells that trigger an immune response when exposed to incompatible blood types.
What factors affect blood donation eligibility?
Factors such as age, weight, health conditions, medications, and travel history can impact blood donation eligibility. To ensure safety, potential donors are screened to minimize any potential risks.
What are the potential risks associated with blood transfusions?
While blood transfusions are generally safe, potential risks include allergic reactions, infections, and transfusion-related lung injury. Careful blood typing and compatibility testing are essential to mitigate these risks.